-
A
Niger
-
B
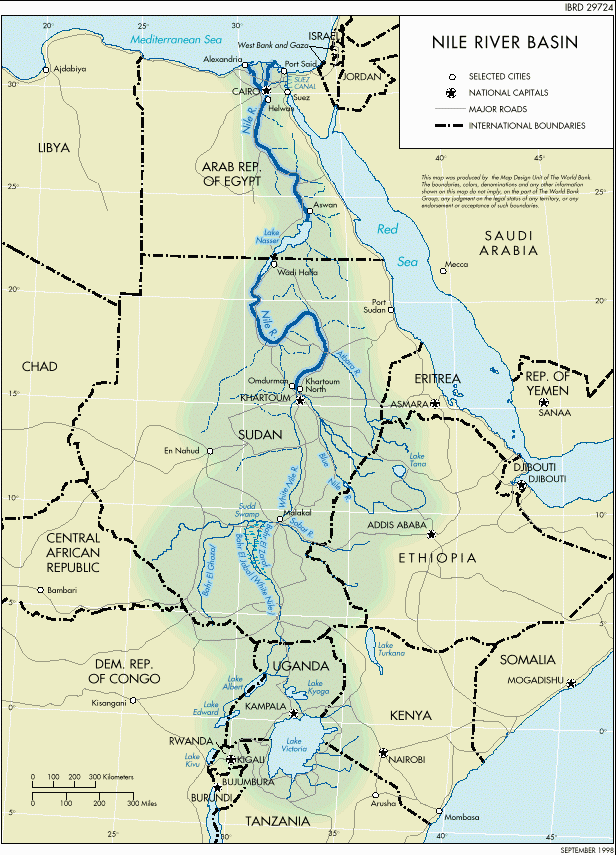
Nile
-
C
Congo
-
D
Zambezi
B
Answer:
B
The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It is commonly regarded as the longest river in the world, though other conflicting sources cite a 2007 study that gave the title to the Amazon River in South America. The Nile, which is 6,853 km (4,258 miles) long, is an "international" river as its drainage basin covers eleven countries, namely, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt and Sudan.
 Antarctica
Antarctica  Galaxy
Galaxy 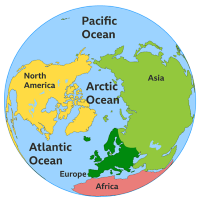 Oceans
Oceans  Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso 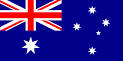 Australia
Australia  Brazil
Brazil  Chile
Chile 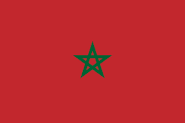 Morocco
Morocco  Tanzania
Tanzania  Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia  United States
United States  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Togo
Togo  Sweden
Sweden  Singapore
Singapore  Switzerland
Switzerland  Argentina
Argentina  Greece
Greece  Cameroon
Cameroon  Spain
Spain  Romania
Romania 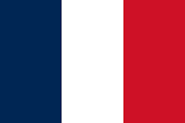 France
France  Mexico
Mexico  Canada
Canada  Guatemala
Guatemala  Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka  Qatar
Qatar  Italy
Italy  Netherlands
Netherlands  Malaysia
Malaysia  Germany
Germany  Poland
Poland  Luxembourg
Luxembourg  Austria
Austria  Finland
Finland