Answer:
A
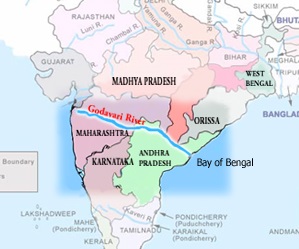
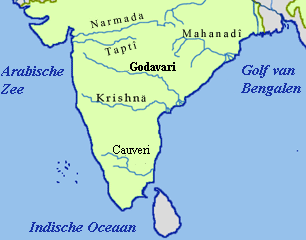
South India, geography, states, union territories, landmarks, beaches, temples, museums, festivals, national parks, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Goa, Maharashtra, Puducherry, Lakshadweep, Kanchipuram, Thiruvithamkoor, Tulu Nadu, Velanadu, Uttarandhra, Western Ghats, Deccan plateau, Sri Lanka, Palk Strait, Rama's Bridge, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Kanyakumari, Mysore Palace, Chettinad Palace, Padmanabhapuram Palace, Hawa Mahal, Agra Fort, Golconda Fort, Gwalior Fort, Gingee Fort, Brihadeeswarar Temple, Somnath Temple, Venkateswara Temple, Konark Sun Temple, Government Museum Chennai, Salar Jung Museum Hyderabad, National Museum New Delhi, Visvesvaraya Industrial and Technological Museum Bengaluru, Bandhavgarh National Park, Periyar National Park, Silent Valley National Park, Kumarakom Bird Sanctuary, Dussehra, Diwali, Onam, Ugadi, Basilica of Bom Jesus, Se Cathedral, Immaculate Conception Cathedral, Church of the Sacred Heart of Jesus, Mahabalipuram Lighthouse, Vypeen Lighthouse, Thiruvananthapuram Lighthouse, Minicoy Lighthouse.

 Indian Temples
Indian Temples  পরিবেশ বিজ্ঞান
পরিবেশ বিজ্ঞান  India
India  North India
North India  Central India
Central India  West India
West India