- A Basal cell carcinoma
- B Squamous cell carcinoma
- C Melanoma
- D Kaposi sarcoma
Answer:
A
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It develops in the basal cells, which are located in the deepest layer of the epidermis. Basal cell carcinoma usually appears as a raised, waxy bump or a flat, scaly lesion with a pearly or translucent appearance. It rarely metastasizes or spreads to other parts of the body, but it can invade nearby tissue and cause significant damage if left untreated.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 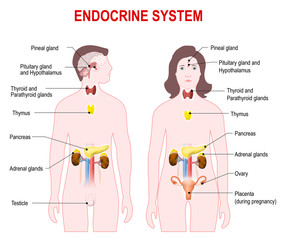 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন