- A Erich Tschemark
- B Carl Correns
- C Gregor Johann Mendel
- D Hugo de Vries
Answer:
C
Gregor Johann Mendel, an Austrian monk, is recognized as the Father of Genetics for his groundbreaking work on inheritance. In 1856, he published his findings on the principles of inheritance, which are now known as Mendel's laws. Although his work was initially overlooked, it was rediscovered by three biologists in 1900.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 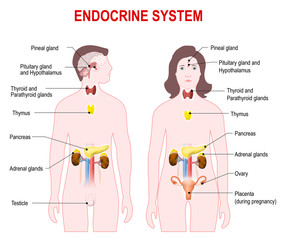 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন