- A Decreasing glycogenolysis
- B Lipogenesis
- C Gluconeogenesis
- D Glycogenesis
Answer:
C
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate the body's metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Insulin promotes the uptake and storage of glucose in cells and inhibits the breakdown of stored glucose, called glycogenolysis. It also stimulates the conversion of glucose to glycogen, known as glycogenesis, and the synthesis of fats from glucose, called lipogenesis. However, insulin does not promote the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids and fats, which is known as gluconeogenesis. This is because insulin signals the body to use glucose as a primary source of energy and to conserve glucose for use in the brain and other essential organs.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 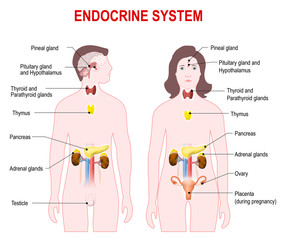 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন