- A Less than carbon dioxide
- B Less than the blood
- C More than the blood
- D Equal to that of the blood
Answer:
C
The partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli is more than that of the blood. This is due to the process of diffusion, where oxygen moves from an area of high concentration (alveoli) to an area of low concentration (blood). Similarly, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveoli is less than that of the blood, as carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the alveoli through diffusion. Therefore, option C is the correct statement.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 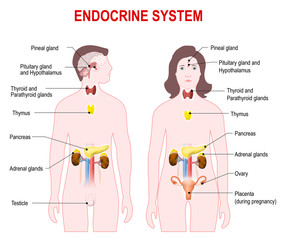 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন