- A Collecting Duct
- B Renal Papilla
- C Distal Convoluted Tubule
- D Glomerulus
Answer:
A
The collecting duct is the last part of the nephron, which is a part of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. The collecting duct receives urine from the distal convoluted tubules of several nephrons and moves it through the renal pyramid to the renal papilla. The renal papilla is the site where urine is drained into the minor calyx, and eventually the major calyx, renal pelvis, and ureter. The collecting duct also plays an important role in the reabsorption of water, which is regulated by the hormone vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone). Overall, the collecting duct plays a crucial role in the kidney's ability to maintain the body's fluid balance and eliminate waste products.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 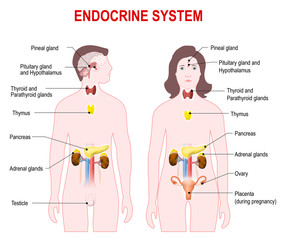 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন