- A Action potential
- B Graded potential
- C Resting potential
- D Membrane potential
Answer:
A
A nerve impulse is also known as an action potential. It is a brief electrical signal that travels along the axon of a neuron, and it is caused by a change in the membrane potential of the neuron. This change in membrane potential, which is known as depolarization, occurs when sodium ions rush into the cell, making the inside more positive. This depolarization then triggers the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels, allowing potassium ions to flow out of the cell, which returns the membrane potential to its resting state. The action potential travels down the axon to the synapse, where it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which carry the signal to the next neuron or effector cell.
 Integumentary system
Integumentary system  Embedded system
Embedded system 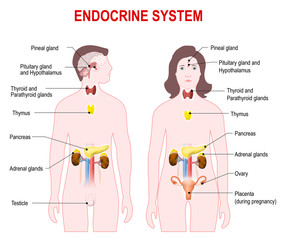 Endocrine system
Endocrine system  জীবদেহের গঠন
জীবদেহের গঠন  কোশের আকৃতি
কোশের আকৃতি  মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি
মানুষের দেহের কোশের আকৃতি  বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ
বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় কাজ  উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ
উদ্ভিদদেহে ও প্রাণীদেহে কোশের কাজের বিশেষত্ব ও কলার প্রকারভেদ  প্রাণীকোশের গঠন
প্রাণীকোশের গঠন