
Types of Nouns in English
Table of Content:
A noun is a word used to name a person, place, thing, or idea.
orNouns are words that identify or name people, places, or things. Nouns can function as the subject of a clause or sentence, an object of a verb, or an object of a preposition. Words like cat, book, table, girl, and plane are all nouns.
A noun is one of the most important words you use when speaking and writing. A noun names a person, place, or thing; a quality, idea, or action.
We can classify or group nouns into the following categories: proper, common, concrete, abstract, collective, and compound nouns. The following chart explains these classifications.
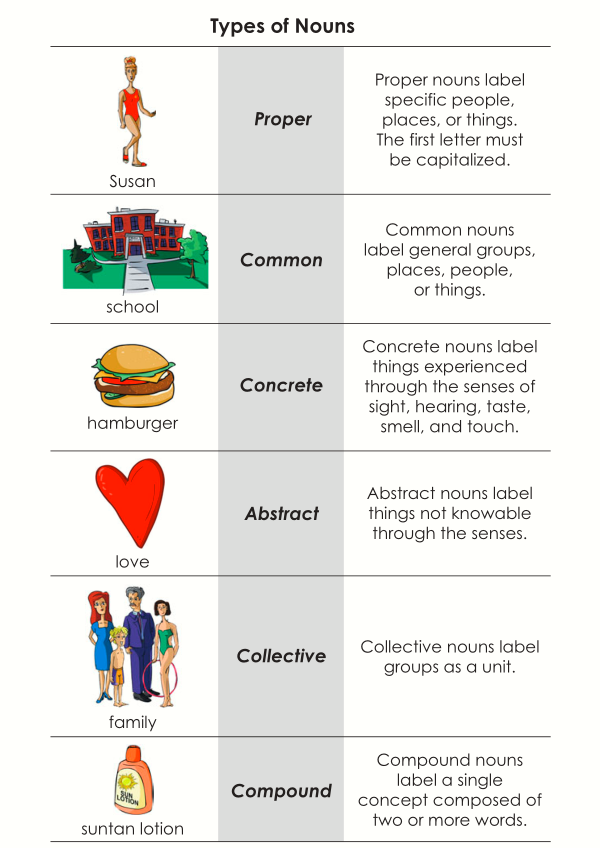
Note: A noun can belong to more than one group. For example, suntan lotion is both a common and a concrete noun, as well as a compound noun.
The highlighted words in the following sentences are all nouns.
- Late last year out neighbour bought a goat.
- Kapil dev was a cricketer.
- The bus inspector locked at all the passengers’ passes.
- Philosophy is of little comfort to the starving.
Noun Gender
Many common nouns, like doctor or teacher, can refer to men or women. Once, many English nouns would change form depending on their gender for example, a man was called an author while a woman was called an authoress but this use of gender-specific nouns is very rare today. Those that are still used occasionally tend to refer to occupational categories, as in the following sentences.
- Ashok Kumar was a very prominent nineteenth-century actor.
- Rekha was at the height of her career as an actress in the 1980s.
- The manager was trying to write an advertisement, but he couldn't decide whether he Was advertising for a waiter or a waitress.
The Subject
The subject in a sentence or clause is the person or thing doing, performing, or controlling the action of the verb. For example:
- • “The dog chased its tail.” (The noun dog is performing the action of the verb chase.)
- • “ Mary reads a book every week.” (The proper noun Mary is performing the action of the verb read.)
Objects
Grammatical objects have three grammatical roles: the direct object of a verb, the indirect object of a verb, or the object of a preposition.
Direct objects
Direct objects are what receive the action of the verb in a sentence or clause. For example:
- • “The dog chased its tail.” (The noun tail is receiving the action of the verb chase.)
- • “Mary reads a book every week.” (The noun book is receiving the action of the verb read.)
Indirect objects
An indirect object is the person or thing who receives the direct object of the verb. For instance:
- • “Please pass Jeremy the salt.” (The proper noun Jeremy is receiving the direct object salt, which receives the action of the verb pass.)
- • “I sent the company an application for the job.” (The noun company is receiving the direct object application, which receives the action of the verb sent.)
Objects of prepositions
Nouns are also used after prepositions to create prepositional phrases. When a noun is part of a prepositional phrase, it is known as the object of the preposition. For example:
- • “Your backpack is under the table.” (The noun table is the object of the preposition under, which creates the prepositional phrase under the table.)
- • “I am looking for work.” (The noun work is the object of the preposition for, which creates the prepositional phrase for work.)