- A Chennai
- B Chandigarh
- C Bhubaneswar
- D Kohima
Answer:
A
Chennai is the capital city of Tamil Nadu. Chennai was earlier known as Madras. Madras was the official name of the city till 1996. Chennai is known as the “Health capital of India”.
 Karnataka GK
Karnataka GK  Bihar GK
Bihar GK  Tamil Nadu GK
Tamil Nadu GK  Gujarat GK
Gujarat GK 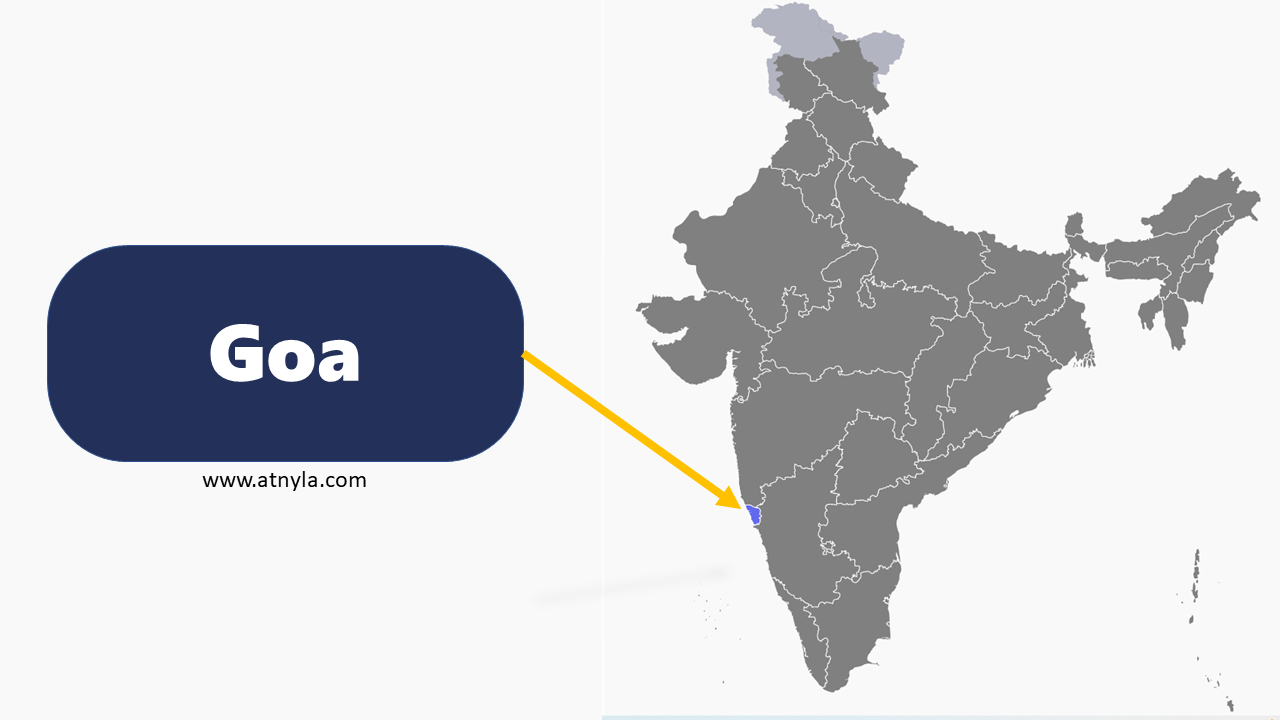 Goa GK
Goa GK 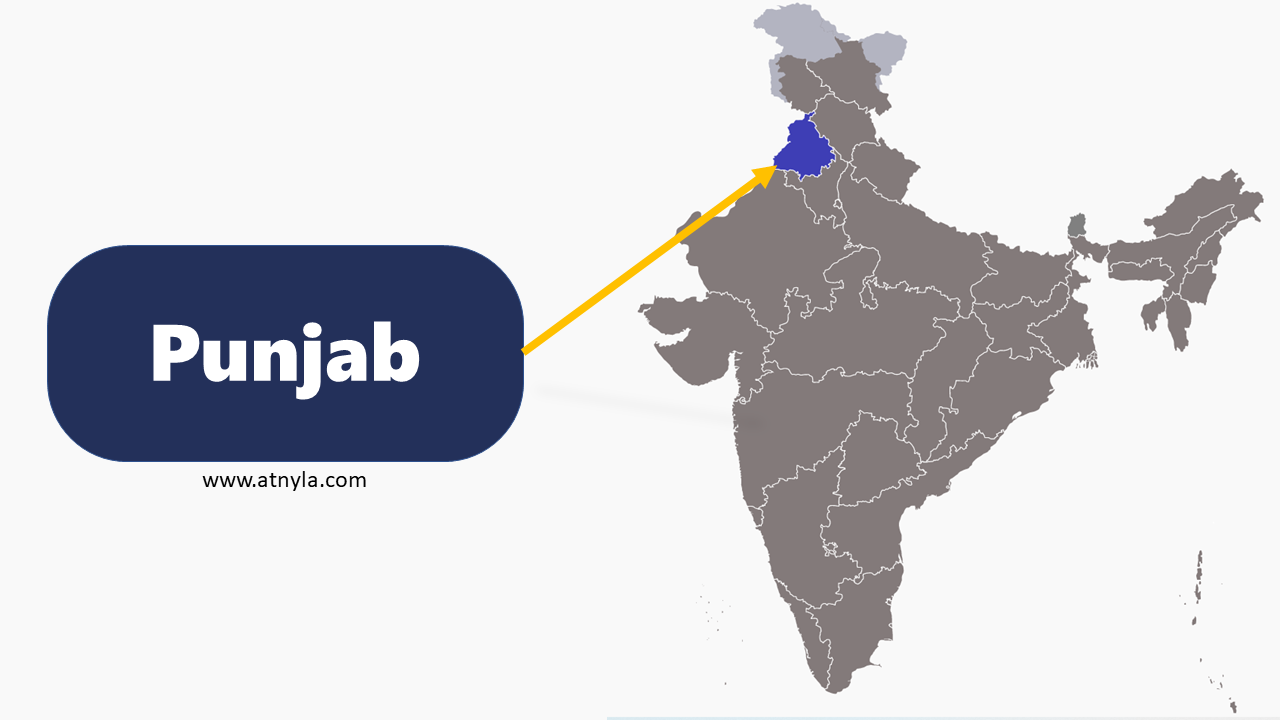 Punjab GK
Punjab GK 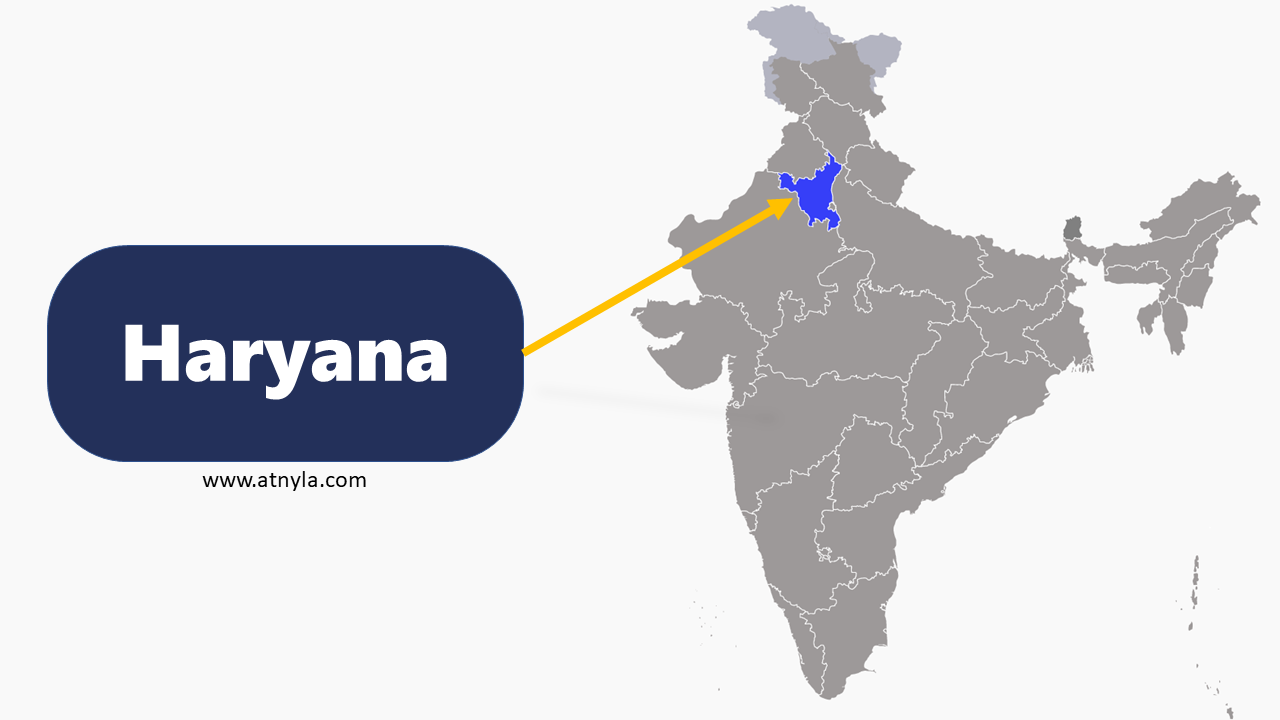 Haryana GK
Haryana GK 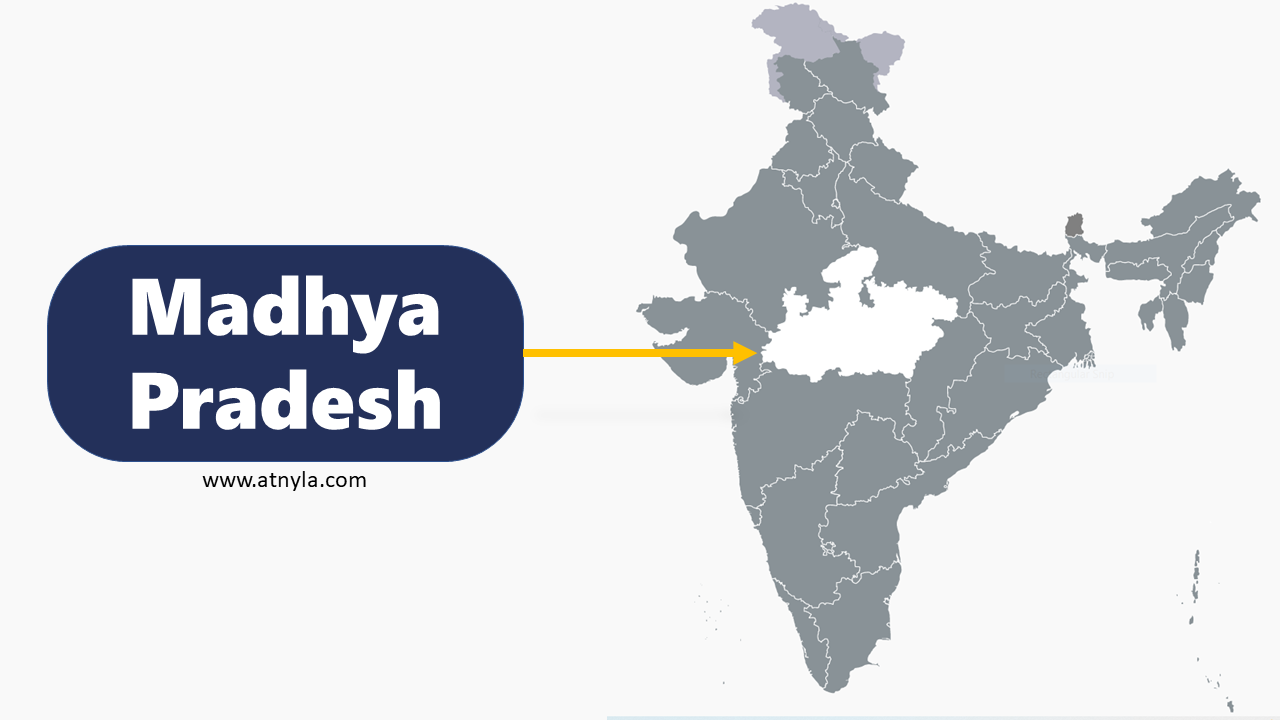 Madhya Pradesh GK
Madhya Pradesh GK 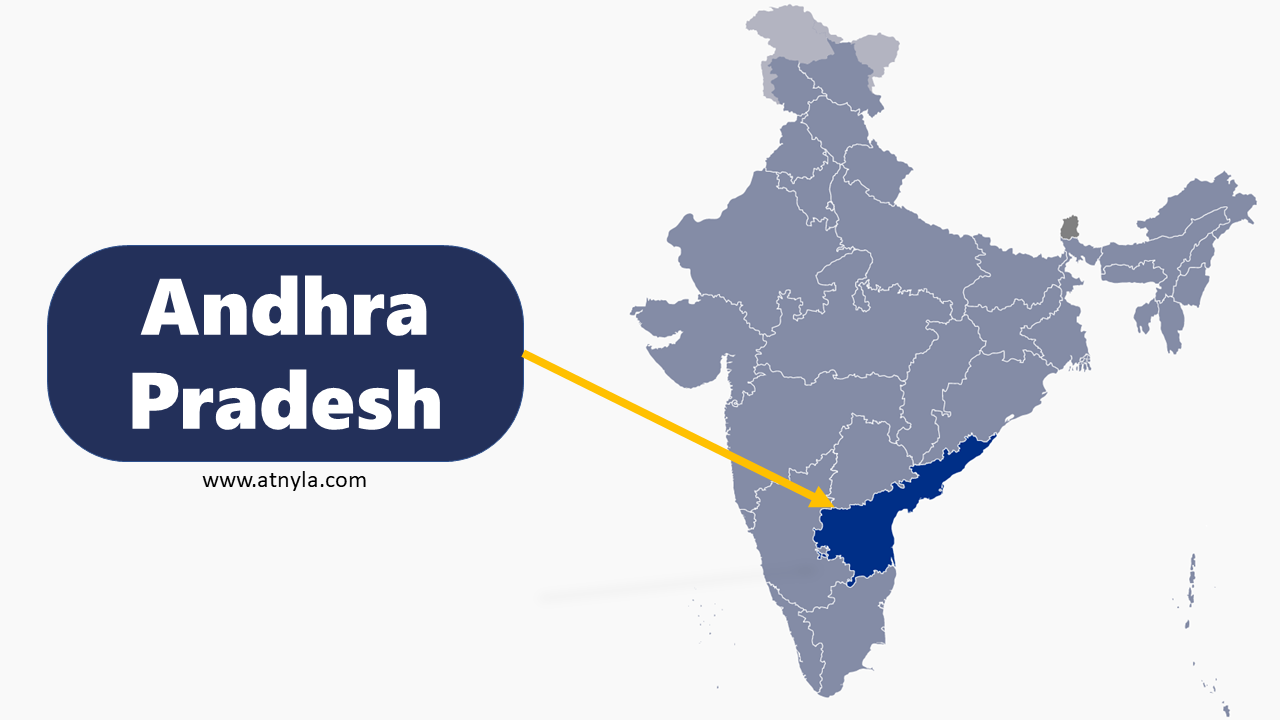 Andhra Pradesh GK
Andhra Pradesh GK 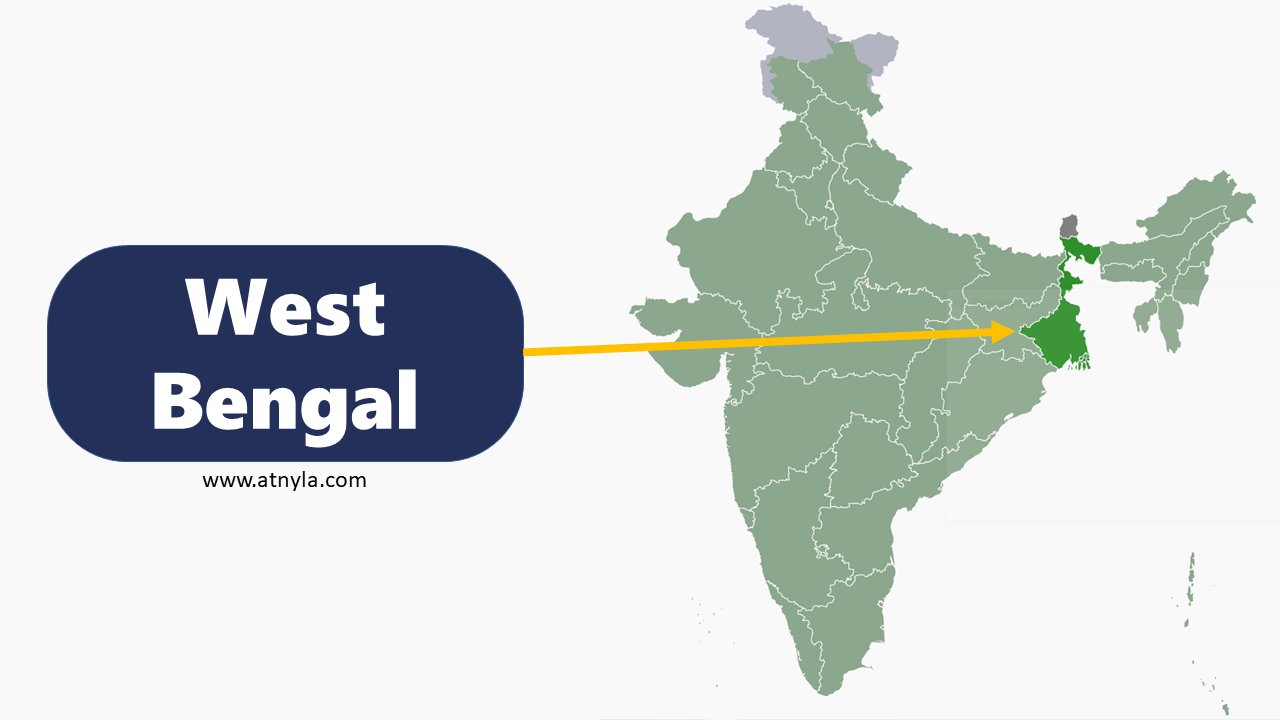 West Bengal GK
West Bengal GK 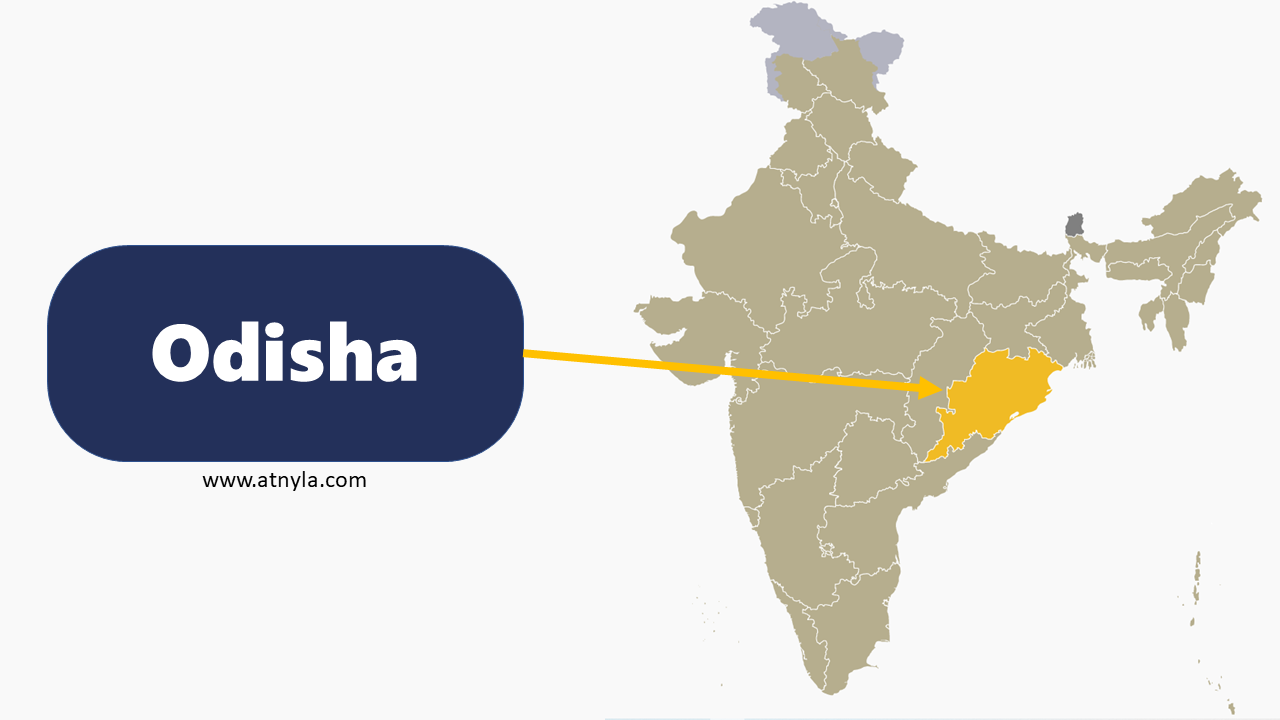 Odisha GK
Odisha GK 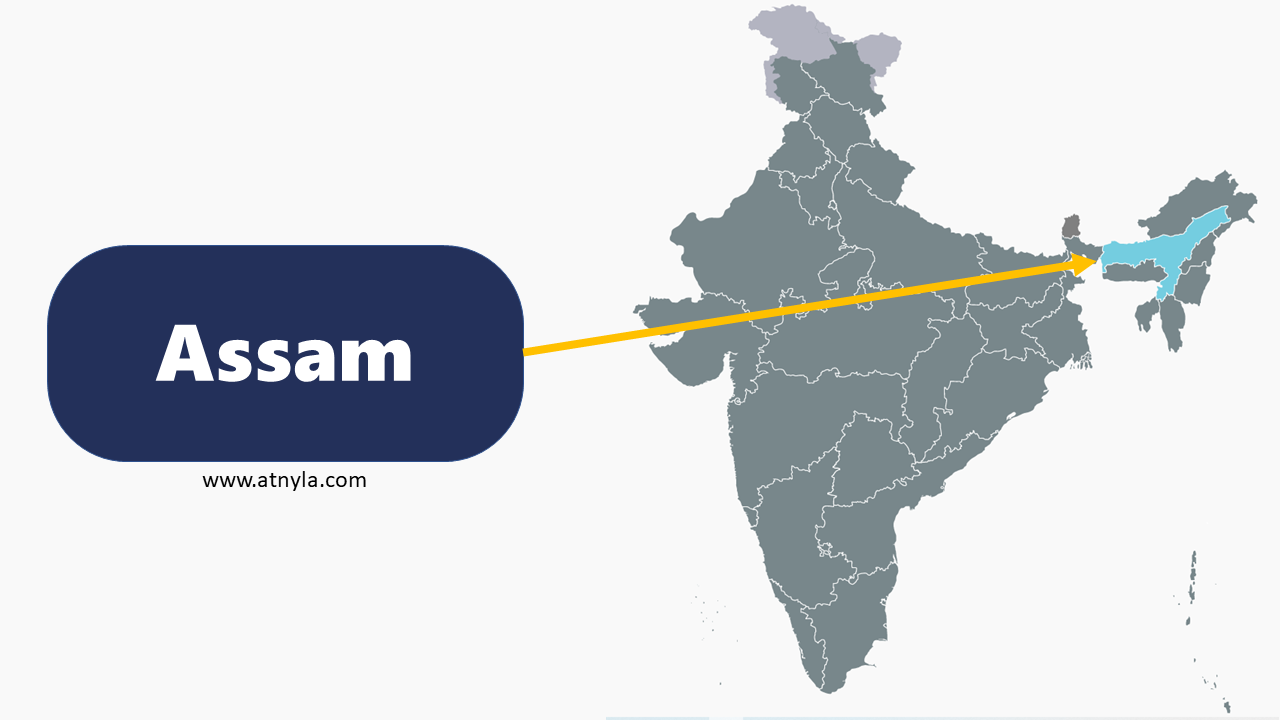 Assam GK
Assam GK  Delhi GK
Delhi GK  Rajasthan GK
Rajasthan GK