
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Table of Content:
What is Artificial Intelligence?
According to the father of Artificial Intelligence, John McCarthy, it is “The science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs”.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a software think intelligently, in the similar manner the intelligent humans think.
AI is accomplished by studying how human brain thinks, and how humans learn, decide, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the outcomes of this study as a basis of developing intelligent software and systems.
What is Artificial Intelligence? AI promises a future where technology is integrated into our environment and adapts to our needs and also frees us from doing repetitive and dangerous tasks
The problem with Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is a general term that describes technologies that make computers, robots and software applications think intelligently. However, defining “Intelligence” is what causes most of the confusion and misunderstanding!
What is the distinction between a computer application that uses rule engines to process different exceptions and one that uses AI to do the same?
Why is AI different?
Applications have always had some form intelligence - using mechanisms such as Rule engines, analytics and models. The crucial insight into why AI approaches are different is the difference between traditional Models and Data-driven Models. AI algorithms use data to improve their logic, unlike earlier approaches that required offline programmatic interventions to change algorithms.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a specific technique within Artificial Intelligence that deals with algorithms that can learn from data.
AI is Interdisciplinary
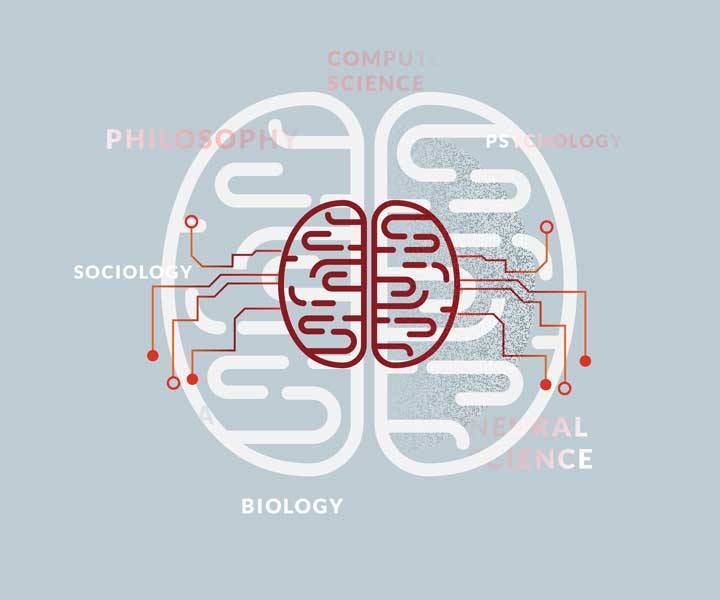
AI is inter-disciplinary by design. It is at the confluence of computer science, psychology, neurological science, biology, mathematics, sociology and anthropology, and philosophy.
What are Artificial Neural Networks?
An artificial neural network, or simply neural network, is a type of artificial intelligence (computer system) that attempts to mimic the way the human brain processes and stores information. It works by creating connections between mathematical processing elements, called neurons. Knowledge is encoded into the network through the strength of the connections between different neurons, called weights, and by creating groups, or layers, of neurons that work in parallel. The system learns through a process of determining the number of neurons or nodes and adjusting the weights for the connections based upon training data. In supervised learning, the training data is composed of input-output pairs. A neural network tries to find a function which, when given the inputs, produces the outputs. Through repeated application of training data, the network then approximates a function for that input domain. There are two main types of neural networks,//xe^i (non-adaptive), and dynamic (adaptive).
Fixed neural networks, sometimes referred to as Pre-Trained Neural Networks (PTNN), are those that have undergone training and then become set. The internal structure of the network remains unchanged during operation. After training is complete, all weights, connections, and node configurations remain the same, and the network reduces to a repeatable fijnction. A common use of a fixed neural network might be a classification system to identify malformed products on a manufacturing line where the definition of an undesirable characteristic would not change and the network would be expected to perform the same classification repeatedly.
Dynamic neural networks, sometimes referred to as Online Learning Neural Networks (OLNN), are never fixed in that the system continues to develop throughout its life. An OLNN is continuously adapting to current data, changing its internal structure of neurons and weights. OLNNs are employed in situations where a system must learn new information while in use. This is usefiil where unforeseen scenarios occur, such as aircraft failures, or when input domains change over time, such as stock market analysis.
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
-
To Create Expert Systems ? The systems which exhibit intelligent behavior, learn, demonstrate, explain, and advice its users.
-
To Implement Human Intelligence in Machines ? Creating systems that understand, think, learn, and behave like humans.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI has been dominant in various fields such as ?
-
Gaming ? AI plays a crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where the machine can think of a large number of possible positions based on heuristic knowledge.
-
Natural Language Processing ? It is possible to interact with the computer that understands the natural language spoken by humans.
-
Expert Systems ? There are some applications which integrate machine, software, and special information to impart reasoning and advising. They provide explanation and advice to the users.
-
Speech Recognition ? Some intelligent systems are capable of hearing and comprehending the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while a human talks to it. It can handle different accents, slang words, noise in the background, change in human’s noise due to cold, etc.
-
Handwriting Recognition ? The handwriting recognition software reads the text written on paper by a pen or on screen by a stylus. It can recognize the shapes of the letters and convert it into editable text.
-
Intelligent Robots ? Robots are able to perform the tasks given by a human. They have sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. They have efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence. In addition, they are capable of learning from their mistakes and they can adapt to the new environment.
-
Vision Systems ? These systems understand, interpret, and comprehend visual input on the computer. For example,
-
A spying airplane takes photographs, which are used to figure out spatial information or map of the areas.
-
Doctors use a clinical expert system to diagnose the patient.
-
Police use computer software that can recognize the face of criminal with the stored portrait made by the forensic artist.
-
AI is already everywhere: Gaming
AI has always played a huge role in gaming. Large, virtual worlds have used AI to generate randomized, yet realistic game situations that are unique for every user using heuristic models.
AI is already everywhere: Natural Language Processing
The arrival of distributed Big Data processing platforms has made the ability to analyze and infer Natural Language using algorithms that have been trained on existing corpus of language samples is now mainstream. We see this everywhere from Siri, Alexa and Google Voice Assistant. The earlier approach of encoding grammar as rules has given way to a more data-driven approach that trains models using real life use of language/s.
AI is already everywhere: Vision Systems

Recent AI techniques such as Deep Learning have enabled
the ability to recognize objects from pictures and videos with more efficiency than human vision! These see usage
in autonomous vehicles and security systems.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is a recent AI technique that uses multi-layered neural networks that has proven to be particularly effective in computer vision. You will learn about neural networks in a subsequent card
AI is already everywhere: Intelligent Robots
From specialised robots, AI has now enabled the first generation of general purpose robots that can be trained by humans to learn general purposes tasks. Amazon, for example, uses Kiva robots in its warehouses. These robots aid in item retrieval before shipping
Get your AI Lingo Right: Part 1
-
Expert systems: Use algorithms such as
Logistic Regression & Support Vector Machinesin situations like flight tracking systems, clinical systems and financial advisory, and automated stock trading applications. -
Natural Language Processing: Algorithms that you can see in day to day applications like Google or Siri’s voice recognition, search engines and sentiment analysis.
Get your AI Lingo Right: Part 2
-
Neural Networks - That use complex data structures that resemble
neuronsin our brains to buildpattern recognition modelsthat learn from input data and reinforce themselves based on errors.Deep Learningis a specific kind ofNeural Networkthat involves using many layers of“neurons”that has recently resulted in huge improvements in areas such as face and object detection, character and handwriting recognition. -
Robotics - Industrial robots for manufacturing situations, such as moving, spraying, painting, precision checking, drilling and coating etc.
Hands-on Exercise: Artificial Intelligence
Go try out Google Autodraw and experience the awesome power of visual computing. It can take your utterly terrible sketches and turn them into beautiful art, exactly the way you wished you could draw
Summary: Artificial Intelligence
-
AI is a set of technologies that combine algorithms and training data to enable complex human-like intelligence in computers.
-
AI techniques have historically been used in Expert tasks such as Financial analysis, Scientific analysis and Diagnosis.
-
The growth of Big Data platforms, cloud based distributed computing technologies has now made it possible to build more complex, general purpose AI for mundane and formal tasks.
-
AI is increasingly everywhere now - in search & recommendation engines, face recognition, robots & self driven vehicles.